Bachelor level courses
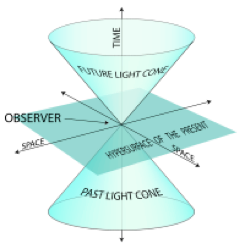
Introduction to special relativity
The lectures were given at Utrecht University
- During this series of lectures, students are introduced to the following:
Concepts of special relativity
Time dilation
Space contraction
Causality
Velocity transformations
Four-vector notation
Covariant and contravariant notations
Invariant quantities
Proper time
Energy-momentum four-vectors
Relativistic collisions
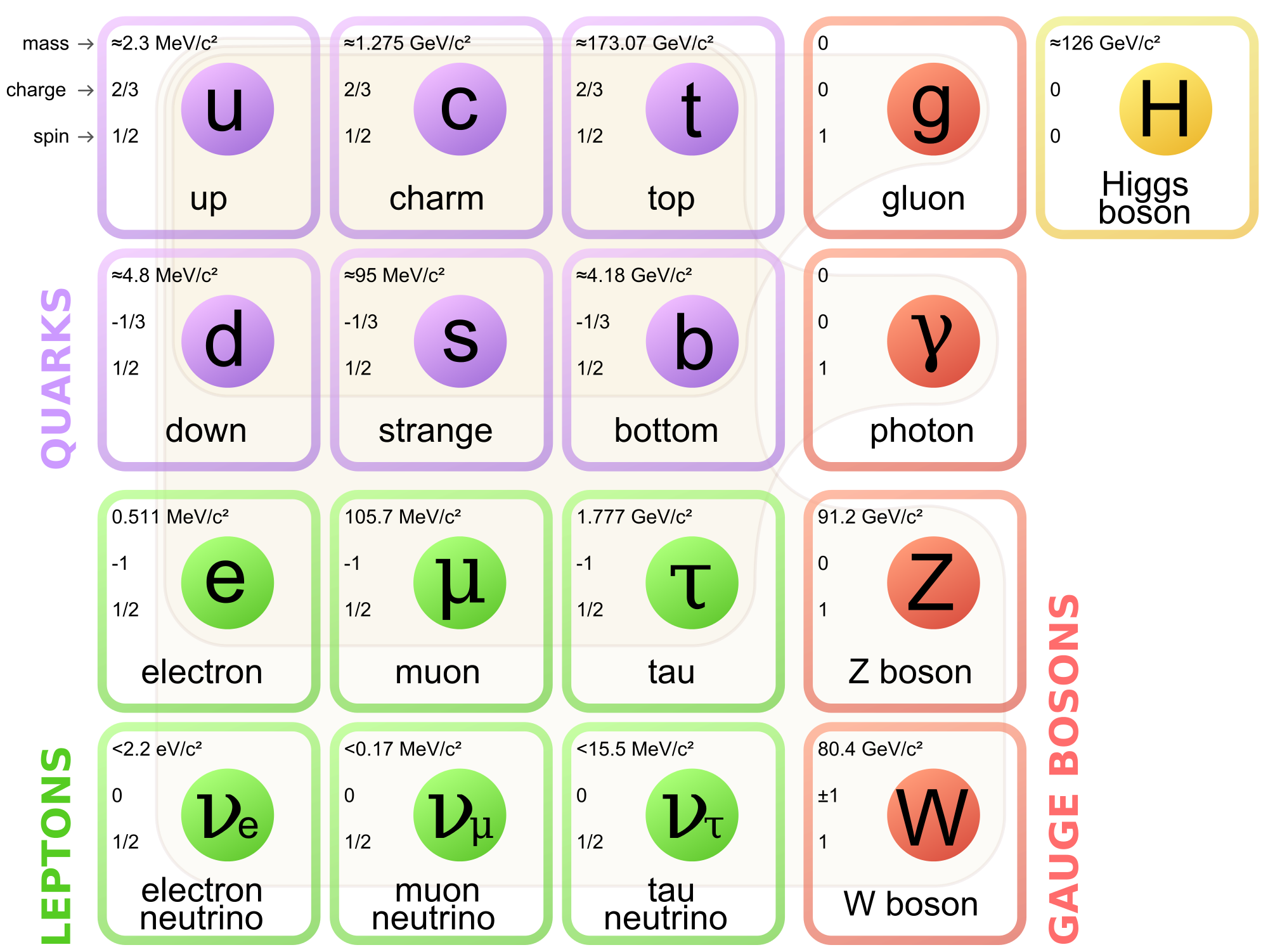
Introduction to elementary particle physics
- Basic information
- The course is part of the curriculum of TU Delft
- It is given in the second block to bachelor students at TU Delft as elective
- The lectures are given at the Aula of TU Delft every Monday, Wednesday and Friday from 13:00 to 15:00 (tutorials between 15:00 and 17:00).
- Grading scheme
- The course has homework that allows you to get max 2 bonus points
- The final grade is estimated as the maximum between the grade from the exams and the weighted average of the grade from the exams and the homework with 80%-20% weight, respectively.
- The grading scheme together with some basic examples on how this works practically can be found here.
- Contents
- The course gives a first flavour to the student about the basic concepts of the Standard Model of particle physics.
- The students will be introduced to:
- Special relativity
- Elements of quantum mechanics
- The interactions of the Standard model
- The particle zoo
- The need for physics beyond the Standard Model
- Interaction of particles with matter, particle detectors and instrumentation
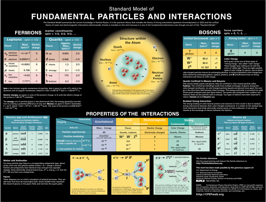
Subatomic Physics
- Basic information
- The course is part of the curriculum of the physics department of UU
- It is given in the second semester to 3rd year bachelor students at UU
- The lectures are given in Utrecht every Wednesday from 13:00 to 15:00 (tutorials between 15:00 and 17:00) and Friday from 09:00 to 11:00 (tutorials between 13:00 and 17:00).
- Prerequisites: Course on quantum mechanics
- Textbook: “Introduction to Elementary Particles”, D. Griffiths

- Grading scheme
- There is a mid-term exam usually scheduled on the 5th week.
- In addition, the course has significant homework that allows you to get max 2 bonus points
- The grade from the exams is calculated as the weighted average of the mid-term and the final exam with 40%-60% weight, respectively.
- The final grade is estimated as the maximum between the grade from the exams and the weighted average of the grade from the exams and the homework with 80%-20% weight, respectively.
- The grading scheme together with some basic examples on how this works practically can be found here.
- Contents
- The course builds up gradually and attempts to introduce the subatomic world as described by the Standard Model, its fundamental particles and their interactions.
- In the course of the semester the students will be introduced to:
- Symmetries, invariances and conservation laws
- Particles (e.g. gauge bosons, leptons, quarks, hadrons) and their properties (e.g. charge, spin magnetic moment)
- Interaction of particles with matter and particle detectors
- Gauge theories
- Quantum Electrodynamics (QED)
- Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD)
- Glashow-Weinberg-Salam theory (weak interactions)
- Spontaneous symmetry breaking and the Higgs mechanism
- Connection between astroparticle and particle physics
- Reading material
- Introduction
- Special relativity and 4-vectors
- Symmetries and conservation laws - slides
- The particle zoo: types of particles and their properties - slides
- Interaction of particles with matter - slides
- Fermi’s golden rule - slides
- Introduction to gauge theories
- QED and the E/M interactions - slides
- Elastic scattering, form factors, charge distributions
- QCD and the strong interactions - slides
- GWS and the weak interactions
- The Higgs mechanism
- Nuclear and particle astrophysics - slides
